Introduction:
Benign tumors, while non-malignant, are abnormal cell clusters that grow slowly and do not spread to other parts of the body. Despite their non-cancerous nature, some of these tumors can lead to functional impairments or cosmetic deformities if left untreated. Among these, bone tumors affecting the jaw—typically originating from mature bone tissue—are of particular clinical significance.
This report discusses a case involving a 22-year-old female patient with a benign bone tumor in the mandibular condyle. The patient underwent thorough diagnostic evaluation followed by early surgical intervention, which resulted in significant improvement in both symptoms and jaw function. Continuous follow-up ensured no postoperative complications.
This case emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and timely surgical treatment of benign bone tumors, particularly those affecting the lower jaw. While these tumors generally pose minimal risk to life, delayed treatment can result in functional issues or cosmetic deformities. Accurate diagnosis and prompt intervention are essential for improving clinical outcomes, minimizing complications, and facilitating full recovery.
Case Presentation
– Patient History:
The patient, G.S., a 22-year-old, presented to the maxillofacial clinic with complaints of facial asymmetry and deviation of the jaw to the left, along with restricted mouth opening. The patient reported that these symptoms had been gradually worsening over the past year. Given the absence of any congenital deformities or childhood abnormalities, the medical team suspected the cause to be related to a tumor or a cyst in the jaw.
– Diagnostic Procedures:
Panoramic radiography of the jaws and contrast computed tomography (CT) were performed. These imaging revealed a tumor in the medial portion of the mandibular condyle.
Following consultations with an oncologist and the completion of routine preoperative tests, the patient was scheduled for surgical excision of the tumor, accompanied by an excisional biopsy to confirm the diagnosis.
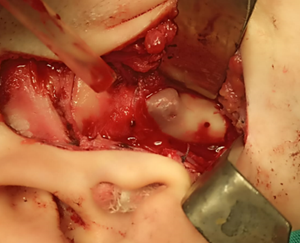
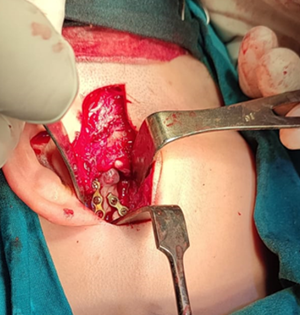
– Surgical Intervention:
After preparing the patient, the tumor was accessed via a preauricular incision, a complex surgical approach due to the risk of damaging branches of the facial nerve. During the procedure, the mandibular condyle was excised along with the tumor, which extended toward the sub-temporal fossa and medial condyle. Special care was taken to preserve the articular disc of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ).
Following tumor removal, the patient’s bite was realigned to its normal position, and stabilization was achieved using two mini metal plates. This ensured proper fixation of the mandibular structures post-surgery.( Hupp R. James, 2019; Yadav, 2021 )
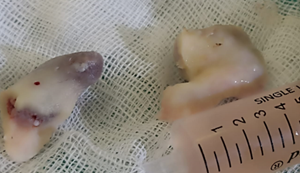
– Follow-up and Treatment:
Postoperatively, the patient was closely monitored in the surgical ward. It was confirmed that there was no significant injury to the branches of the facial nerve, with only minor trauma observed in the frontal branch. The excised tumor sample was sent to the pathology laboratory for further analysis to confirm the tumor’s nature.( Dolan, 2016; Yadav, 2021 )
– Results:
Twenty days post-surgery, the patient returned to the maxillofacial clinic for a follow-up evaluation. The examination revealed a significant improvement in mouth opening, along with a marked restoration of facial symmetry.
– Disclaimer:
This case was managed by Dr. Muhammad Saeed Al-Hamdo, a resident in the Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery specialty, under the supervision of Dr. Ahmed Koja, a member of the Scientific Council, at Idlib Central Hospital, supported by the Syrian American Medical Society (SAMS).
Read more about benign jaw tumors
– References:
Dolan, R. W. (2016). Surgical approaches to the facial skeleton in Trauma. In Facial Plastic, Reconstructive and Trauma Surgery. https://doi.org/10.1201/b14824-17
Hupp R. James. (2019). Contemporary Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 7 th Edition. In Philadelphia.Elsevier.
Yadav, A. (2021). Principles of Internal Fixation in Maxillofacial Surgery. In Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery for the Clinician. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-1346-6_51